Performance optimization is essential for providing a seamless and efficient user experience for enterprise-level applications. ASP.NET Core, known for its speed and scalability, greatly benefits from distributed caching. By implementing distributed caching, applications can reduce database load, improve response times, and ensure scalability. In this blog, we will explore how to enhance ASP.NET Core performance using distributed caching and introduce IDistributedCache as a standardized approach for integrating caching solutions like NCache.
Key Takeaways
- Distributed Caching: Enhances ASP.NET Core performance by reducing database load and improving response times.
- IDistributedCache Interface: Provides a standard API for storing and retrieving data, allowing easy integration with providers like NCache.
- Scalability: Allows data to be stored across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and reliability for high-traffic apps.
- Implementation: Requires installing the NCache NuGet package and registering it in cs.
Understanding Distributed Caching in ASP.NET Core
Distributed caching lets applications store data across different servers instead of in a single in-memory cache. This ensures reliability, scalability, and high availability while reducing its database dependency. By employing a distributed cache, your application can achieve:
- Faster Data Retrieval: Reduces latency by serving frequently accessed data from cache.
- Lower Database Load: Minimizes database queries, improving database efficiency.
- Scalability: Supports high-traffic applications by distributing cache loads.
- Enhanced Application Reliability: Guarantees consistent performance even during database failures.
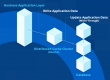
An ASP.NET Core built-in interface called IDistributedCache allows applications to store and retrieve data from a distributed cache. It helps ensure consistency and reliability by allowing cache persistence across multiple nodes. Moreover, implementing IDistributedCache simplifies caching integration with providers like NCache.

Figure: High-Level Distributed Caching Architecture with NCache.
Configuring NCache as an IDistributedCache Provider
NCache is a high-performance, in-memory distributed caching solution that integrates seamlessly with IDistributedCache. To configure and use NCache in your ASP.NET Core application, follow the steps below:
1. Install NCache NuGet Package
To begin, install the NCache package in your application (based on your chosen NCache version):
|
1 |
Install-Package NCache.Microsoft.Extensions.Caching -version x.x.x |
2. Configure NCache in the Program.cs
Modify Program.cs to register NCache as the IDistributedCache provider using the AddNCacheDistributedCache method:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); builder.Services.AddNCacheDistributedCache(options => { options.CacheName = "demoCache"; }); var app = builder.Build(); app.Run(); |
Using IDistributedCache for Common Caching Operations
Once configured, you can inject IDistributedCache into your application to perform common caching operations, such as storing, retrieving, and removing cached data.
Storing and Retrieving Cached Data
The following example implements the Cache-Aside pattern to store and retrieve data. It uses GetAsync to check the cache and SetAsync to populate it if data is missing.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
public class HomeController : Controller { private readonly IDistributedCache _cache; public HomeController(IDistributedCache cache) { _cache = cache; } public async Task<IActionResult> Index() { string cacheKey = "currentTime"; byte[]? cachedTimeBytes = await _cache.GetAsync(cacheKey); string cachedTime = cachedTimeBytes != null ? Encoding.UTF8.GetString(cachedTimeBytes) : null; if (cachedTime == null) { cachedTime = DateTime.Now.ToString(); var options = new DistributedCacheEntryOptions().SetSlidingExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5)); byte[] timeBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(cachedTime); await _cache.SetAsync(cacheKey, timeBytes, options); } ViewBag.CurrentTime = cachedTime; return View(); } } |
Removing Cached Data
You can remove cached data as demonstrated below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public async Task<IActionResult> ClearCache() { string cacheKey = "currentTime"; await _cache.RemoveAsync(cacheKey); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } |
Caching Complex Objects
To cache complex objects, you must serialize them into byte arrays (e.g., using JsonSerializer) before storing them in IDistributedCache:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
public async Task<IActionResult> CacheComplexObject() { string cacheKey = "product"; byte[]? cachedProductBytes = await _cache.GetAsync(cacheKey); Product? product = cachedProductBytes != null ? JsonSerializer.Deserialize<Product>(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(cachedProductBytes)) : null; if (product == null) { product = new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Laptop", Price = 1200 }; var options = new DistributedCacheEntryOptions().SetSlidingExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10)); byte[] productBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(JsonSerializer.Serialize(product)); await _cache.SetAsync(cacheKey, productBytes, options); } return View(product); } |
Conclusion
By integrating NCache with IDistributedCache, ASP.NET Core applications can efficiently manage data caching, reduce database load, and enhance performance. Whether caching simple strings or complex objects, IDistributedCache ensures seamless data retrieval across multiple servers, improving scalability and reliability.
For more details on NCache implementation and best practices, visit the official documentation:
Implementing these caching strategies will ensure your applications run efficiently, handling high-traffic loads while maintaining optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the benefit of using IDistributedCache over in-memory caching?
A: Unlike in-memory caching which is tied to a single server, IDistributedCache stores data across multiple servers, ensuring data survives application restarts and is consistent across a web farm.
Q: How does NCache improve ASP.NET Core performance?
A: NCache reduces latency by caching frequently accessed data in memory and minimizes database bottlenecks, allowing the application to handle more requests.
Q: Can I store complex objects in IDistributedCache?
A: Yes, but they must be serialized (e.g., into JSON or byte arrays) before storage and deserialized upon retrieval.