In modern distributed applications, efficient communication between components is essential for ensuring scalability and responsiveness. The Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) messaging model provides a robust method to decouple message producers and consumers, allowing for asynchronous and scalable interactions. This blog explores the fundamentals of Pub/Sub messaging in .NET applications, its benefits, and demonstrates how to implement it using NCache as an example.
Understanding Pub/Sub Messaging
The Pub/Sub pattern consists of several key components:
- Publishers: Entities responsible for generating and sending messages to a topic without knowing the subscriber.
- Subscribers: Consumers who register their interest in messages from a specific topic and receive them asynchronously.
- Topic: A communication channel through which messages are routed. Publishers and subscribers use topics to send and receive messages.
- Message: The unit of communication containing the actual data object sent by publishers and delivered to subscribers.
- Broker (NCache in this case): Manages message distribution, ensuring efficient and reliable delivery to all subscribed entities.
- Routing: Ensures messages reach the appropriate subscribers based on topic subscriptions.
Such decoupling of publishers and subscribers allows for a scalable, high-performance messaging system ideal for real-time applications and distributed architectures.
Benefits of NCache Pub/Sub Messaging
The benefits of Pub/Sub Messaging with NCache are as below:
- Fast In-Memory with Persistence: It combines the speed of in-memory messaging with persistence for reliability, if necessary.
- Scalability: It easily accommodates multiple publishers and subscribers without direct dependencies.
- Decoupling: It allows publishers and subscribers to operate independently, promoting modular architecture.
- Asynchronous Communication: It also facilitates non-blocking interactions, improving system responsiveness.
- Flexibility: It allows you to add or remove subscribers dynamically without impacting publishers.
- 100% Native .NET: It is fully optimized for .NET applications, ensuring seamless integration and performance.

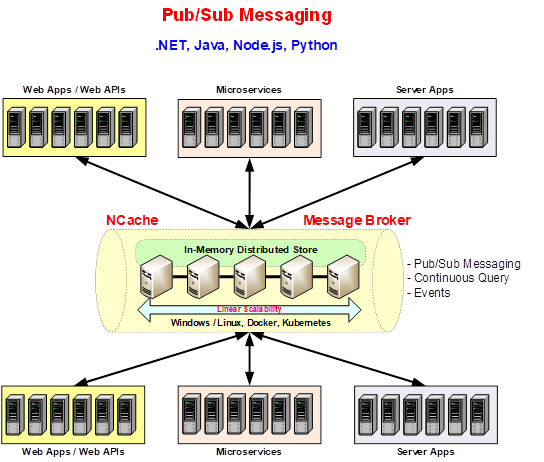
Figure: Pub/Sub Messaging in NCache
Implementing Pub/Sub in .NET with NCache
NCache supports the Pub/Sub messaging model, allowing for efficient communication in distributed applications. Follow the steps below to seamlessly implement Pub/Sub in your .NET applications with NCache.
Setting Up NCache
- Install NCache NuGet Package using PowerShell:
Open Package Manager Console in Visual Studio and run the following command (based on chosen NCache Edition, i.e., Enterprise, Professional, or OpenSource):
- Configure NCache in Your Application:
Run the following code to configure NCache in your application.
Creating a Topic
After configuring NCache in your application, you need to create a topic through which messages are published and subscribed, as follows:
Publishing Messages
Once a topic is created, the publisher can publish messages to that topic, irrespective of its subscriber.
Subscribing to Messages
Next, the subscribers subscribe to the topic of their interest.
Advanced Features
NCache’s Pub/Sub implementation offers advanced features such as:
- Durable Subscriptions: In such type of subscription, a subscriber receives all messages, even in case of disconnectivity.
- Message Expiration: The publisher can set expiration for messages to prevent stale data consumption.
- Pattern-Based Subscription: You can subscribe to single/multiple topics falling under the provided pattern using the pattern-based subscription where NCache supports multiple wildcards.
For detailed information, refer to the NCache Pub/Sub Documentation.
Conclusion
As discussed, implementing Pub/Sub messaging in .NET applications enhances scalability, decouples components, and facilitates efficient asynchronous communication. NCache provides a robust platform to implement this pattern, ensuring high performance and reliability in distributed environments.
By leveraging Pub/Sub messaging with NCache, developers can build responsive and scalable .NET applications that handle real-time data efficiently.