LINQ Support in NCache
Real-world applications may frequently need to filter data rather than simply querying for the primary key. Using LINQ makes it easy to retrieve data from your database based on whatever custom logic you employ at runtime. Therefore, NCache supports LINQ querying, which allows you to query your distributed cache in the same manner you query your database.
LINQ is a generic .NET query language that allows you to search and filter out data from your data source. LINQ syntax is quite similar to SQL, but in functionalities, it provides you with better and more optimized querying methods when querying your NCache servers. It offers the ability to allow more efficient query expressions while catering to syntax checking during code compilation.
NCache seamlessly integrates LINQ to query information within the cache via a LINQ provider. The link provider facilitates the execution of LINQ queries over the distributed cache while improving the application’s performance without changing the LINQ object model.
Supported Querying Expressions
NCache supports LINQ language’s basic querying expressions to search cache data. They are:
- Lambda expressions: Lambda expressions in a LINQ equation translate logic at runtime so it can pass on the data source conveniently.
IQueryable<Product> products = new NCacheQuery<Product>(cache);
IQueryable<Product> product = products.Select(p => p).Where(p => p. UnitsInStock > 10);IQueryable<Product> products = new NCacheQuery<Product>(cache);
IQueryable<Product> product = from prod in products
where prod.UnitsInStock > 10
select prod;LINQ Operators
LINQ operators are extension methods that offer query capabilities like projection, aggregation, filtering, and sorting. Among these operators, NCache supports the ones mentioned below:
- Projection operator: projects values based on a transform function. The following code snippet shows how to use the select projection operator to search cache data.
IQueryable<Product> product = products.Select(prod => prod);IQueryable<Product> product = products.Select(prod => prod).Where(prod => prod.UnitsInStock > 10);Query Operators
NCache supports basic query operators with LINQ querying like:
- Equals (==)
- Not Equals (!=)
- Less Than (<)
- Greater Than (>)
- Less Than Equal To (<=)
- Greater Than Equal To (>=)
Refer to LINQ Query Operators for the usage of these operators.
Logical Operators
NCache supports two logical operators with LINQ - the AND (&&) and OR (||) operators. These operators combine two or more restriction criteria for the cache search. Follow our guide on LINQ Logical Operators to understand their usage in detail.
Aggregation Operators
NCache supports the following aggregation operators:
- Count
- Max
- Min
- Average
- Sum
The following is an example of how to use aggregate functions to search for cache data and count the results:
int count = products.Select(p => p).Where(prod => prod.UnitsInStock <= 50).Count();Understand the usage of aggregate operators in NCache from our guide on LINQ Aggregate Operators.
Wildcard Operators
NCache supports multiple wildcards in LINQ expressions. These wildcard operators are:
- StartsWith
- EndsWith
- Contains
- Equals
The following is an example of using wildcards with a restriction where the operator searches for a specific data set in the cache:
IQueryable<Product> product = products.Select(p => p).Where(p => p.ProductName.StartsWith("Be"));Refer to our documentation on LINQ Wildcard Operators to know more.
LINQPad Support
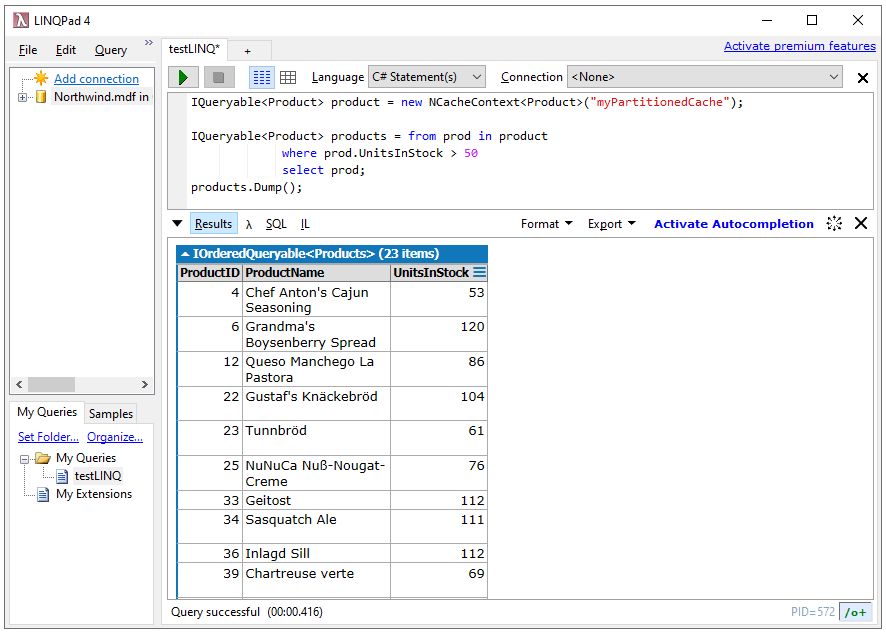
LINQPad is a third-party tool used to interactively query SQL databases using query and lambda expressions and write C# codes without any IDE. NCache supports seamless integration with the LINQPad utility to improve data analysis and application performance. To process queries in LINQPad, NCache LINQ Provider uses the NCacheContext class, which is an implementation of the .NET framework’s IQueryable interface.
IQueryable<Product> product = new NCacheContext<Product>("myPartitionedCache");
IQueryable<Product> products = from prod in product
where prod.UnitsInStock > 50
select prod;
products.Dump();Running this script in the LINQPad will create a LINQ object product to query the products with UnitsInStock greater than 50.
To know more on how to use LINQPad to query data in cache, follow our documentation on Query Data in Cache with LINQPad, and to configure LINQPad in NCache for yourself, follow the steps provided in Configure LINQPad for NCache.
What to Do Next?
Review NCache FeaturesDownload NCache
Request a Personalized LIVE Demo